Corporate Sustainability Strategy: Building a Resilient Future
In todays rapidly changing world, corporate sustainability has become a vital strategy for businesses seeking to thrive while addressing the pressing challenges of environmental degradation and social inequity. A well-crafted corporate sustainability strategy not only enhances a company’s reputation but also contributes to long-term profitability and resilience. This article will explore the essential components of a corporate sustainability strategy, guiding organizations on their journey towards a more sustainable future.
Understanding Corporate Sustainability
Definition of Corporate Sustainability
Corporate sustainability refers to a business approach that creates long-term consumer and employee value while preserving natural resources, the environment, and the community. This strategy integrates economic, environmental, and social goals to ensure that business operations do not compromise future generations’ ability to meet their needs.
Importance of Sustainability in Business
The significance of sustainability in business can be summarized through the following points:
- Risk Management: Companies that adopt sustainable practices can better manage risks associated with environmental regulations, resource scarcity, and social unrest.
- Enhanced Brand Loyalty: Todays consumers are increasingly conscious of the social and environmental impacts of their purchases. A strong sustainability strategy can build trust and loyalty among customers.
- Attracting Talent: Organizations known for their sustainability efforts are often more attractive to potential employees who seek purpose-driven work environments.
Key Principles of Corporate Sustainability
To develop an effective sustainability strategy, businesses should adhere to several key principles:
Environmental Stewardship
This principle emphasizes the importance of reducing environmental impact through practices such as:
- Minimizing waste and pollution
- Conserving energy and water
- Promoting biodiversity
Social Responsibility
Companies must consider the social implications of their actions. This includes:
- Ensuring fair labor practices
- Supporting local communities
- Promoting diversity and inclusion
Economic Viability
While pursuing sustainability, businesses must also ensure their operations remain economically viable. This means:
- Achieving profitability while implementing sustainable practices
- Investing in sustainable innovations that can lead to cost savings
Developing a Corporate Sustainability Strategy
Assessing Current Practices
Before implementing a sustainability strategy, organizations must assess their current practices to identify areas for improvement.
Conducting a Sustainability Audit
A sustainability audit evaluates a company’s operations against sustainability benchmarks. This process typically involves:
- Reviewing resource usage (energy, water, materials)
- Analyzing waste management practices
- Assessing social impacts (community relations, employee engagement)
Identifying Stakeholder Expectations
Understanding the expectations of stakeholderscustomers, employees, investors, and the communityis crucial. Engaging with these groups can provide valuable insights into what sustainability means for your organization.
Setting Sustainability Goals
Once a company has assessed its current practices and stakeholder expectations, it can set meaningful sustainability goals.
Short-term vs. Long-term Goals
Setting both short-term and long-term goals is vital for a successful strategy. Short-term goals provide immediate focus, while long-term goals ensure sustainable growth and development.
SMART Goals Framework
Using the SMART criteriaSpecific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-boundcan help organizations set effective sustainability goals. For example:
- Specific: Reduce carbon emissions by 30%
- Measurable: Track emissions through regular audits
- Achievable: Implement energy-efficient technologies
- Relevant: Align with corporate values
- Time-bound: Achieve this goal by 2025
Integrating Sustainability into Business Operations
Integrating sustainability into everyday operations ensures that it becomes a core aspect of the companys culture.
- Supply Chain Management: Evaluate suppliers for their sustainability practices. Partnering with eco-conscious suppliers can enhance overall corporate sustainability.
- Product Design: Consider sustainable materials and processes during product development to minimize environmental impact.
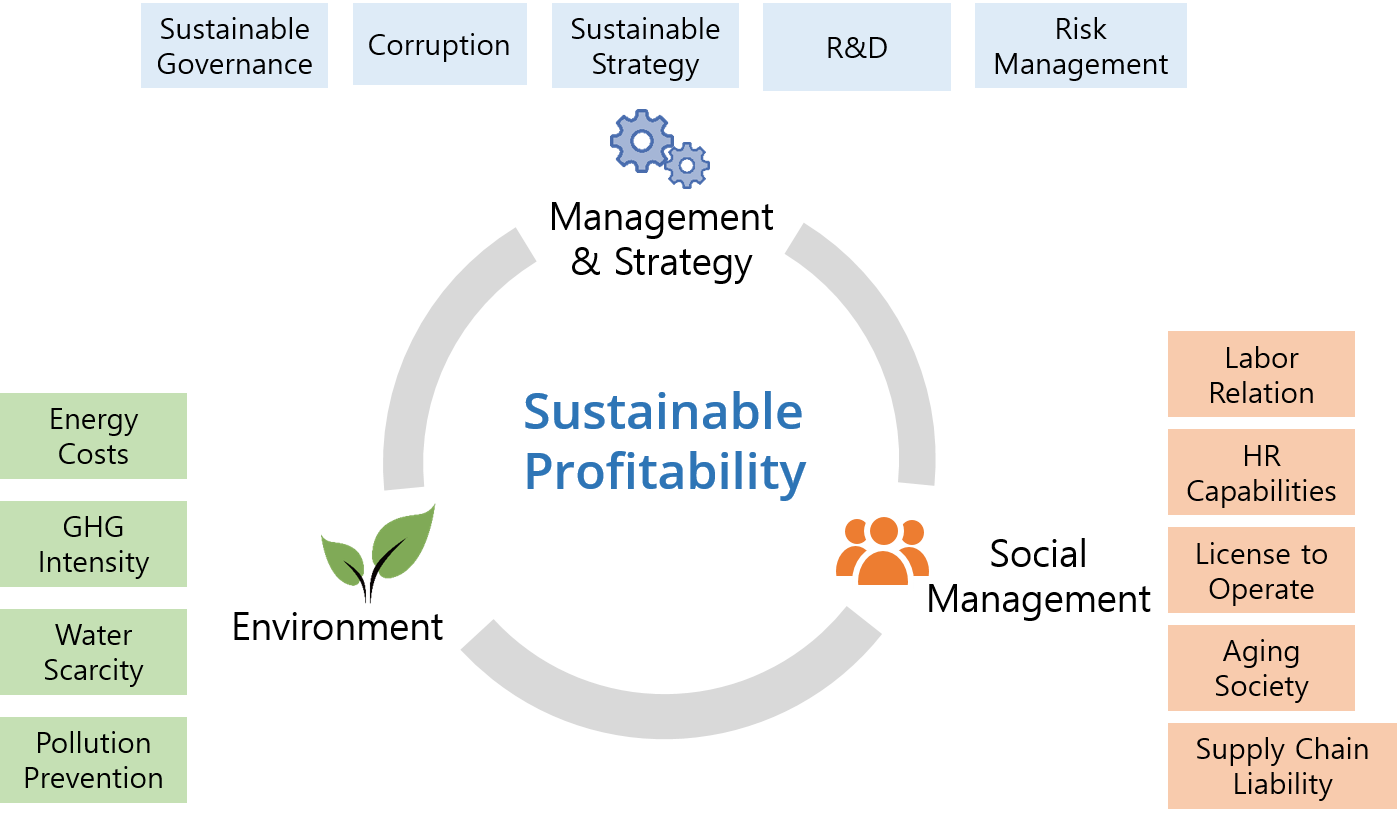
Implementation of Sustainability Strategies
Employee Engagement and Training
Engaging employees is crucial for the successful implementation of a sustainability strategy.
Creating a Sustainability Culture
Establishing a culture of sustainability within the organization encourages employees to participate actively in sustainability initiatives. Strategies for building this culture include:
- Leadership Commitment: Leadership must demonstrate commitment to sustainability, setting the tone for the rest of the organization.
- Incentives: Recognizing and rewarding employees for their sustainability efforts can motivate participation.
Training Programs and Workshops
Providing training on sustainability practices equips employees with the knowledge and skills to contribute effectively. Workshops can cover topics such as:
- Waste reduction techniques
- Sustainable procurement practices
- Energy-saving initiatives
Monitoring and Reporting Progress
To ensure the effectiveness of sustainability strategies, organizations must establish mechanisms for monitoring and reporting progress.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Defining KPIs helps track performance against sustainability goals. Examples of relevant KPIs include:
- Carbon footprint reductions
- Waste diversion rates
- Employee engagement levels in sustainability initiatives
Sustainability Reporting Standards
Adopting recognized sustainability reporting standards, such as the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) or Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), can enhance transparency and credibility.
In the next section, we will explore the challenges organizations face when implementing corporate sustainability strategies and best practices for overcoming these obstacles. Stay tuned to learn how to navigate the complexities of corporate sustainability effectively.
Challenges in Corporate Sustainability
Despite the numerous benefits of implementing a corporate sustainability strategy, organizations may encounter several challenges along the way.
Resistance to Change
One of the most significant hurdles companies face is resistance to change. Employees may be hesitant to adopt new practices, particularly if they perceive them as disruptive to established routines. To overcome this resistance, organizations should:
- Communicate the Vision: Clearly articulate the reasons for adopting sustainability initiatives, emphasizing the benefits for both the company and its stakeholders.
- Involve Employees: Encourage employee involvement in sustainability planning and implementation to foster ownership and acceptance.
Resource Allocation
Implementing a comprehensive sustainability strategy often requires significant resources. Organizations may struggle with:
- Budget Constraints: Limited budgets can hinder the ability to invest in sustainable technologies or training programs.
- Competing Priorities: Balancing sustainability efforts with other business priorities can be challenging. To address this, companies should:
- Prioritize Initiatives: Focus on initiatives that align with overall business goals and offer the highest return on investment.
- Seek External Funding: Explore grants or partnerships that can provide financial support for sustainability projects.

Best Practices for Successful Corporate Sustainability
To enhance the likelihood of a successful sustainability strategy, organizations should consider the following best practices:
Collaboration and Partnerships
Building collaborative relationships with other organizations can amplify sustainability efforts. Partnerships with NGOs, government agencies, and even competitors can lead to shared knowledge and resources, creating a more substantial impact.
- Cross-industry Initiatives: Participate in industry coalitions focused on sustainability challenges to share best practices and drive change at a broader level.
Innovation and Technology Integration
Embracing innovation and technology can significantly enhance sustainability efforts. Companies should:
- Invest in Research and Development: Allocate resources towards developing new, sustainable technologies that can reduce environmental impact.
- Leverage Data Analytics: Use data analytics to track sustainability metrics, optimize resource usage, and identify areas for improvement.
Case Studies of Successful Sustainability Strategies
Examining real-world examples of successful corporate sustainability initiatives can provide valuable insights. Here are a few notable case studies:
- Unilever: This multinational consumer goods company has made substantial strides in sustainability by setting ambitious goals, such as halving its environmental footprint by 2030. Unilever’s Sustainable Living Plan integrates sustainability into its business model, driving innovation and consumer engagement.
-
Patagonia: Known for its environmental activism, Patagonia has built its brand around sustainability. The company uses recycled materials, promotes fair labor practices, and encourages customers to repair rather than replace their products. This commitment not only resonates with consumers but also sets a high standard within the industry.
FAQs About Corporate Sustainability Strategy
Q1: What are the primary benefits of implementing a corporate sustainability strategy?
A1: The primary benefits include risk mitigation, enhanced brand loyalty, improved employee engagement, and long-term profitability. A well-implemented sustainability strategy can also lead to operational efficiencies and a positive impact on the community and environment.
Q2: How can a company measure the success of its sustainability initiatives?
A2: Companies can measure success through Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) such as reductions in carbon emissions, waste diversion rates, energy consumption, and employee engagement levels. Regular sustainability audits and reporting standards can also provide valuable insights.
Q3: What role does leadership play in corporate sustainability?
A3: Leadership is crucial in driving sustainability initiatives. Leaders must demonstrate commitment, set clear goals, and create a culture that prioritizes sustainability within the organization. Their involvement can inspire employees and stakeholders to actively engage in sustainability efforts.
Conclusion
In summary, a corporate sustainability strategy is essential for businesses seeking to thrive in today’s environmentally conscious marketplace. By understanding the importance of sustainability, developing a robust strategy, and overcoming challenges, organizations can enhance their resilience and create long-term value.
Recap of Key Points
- Sustainability Audit: Conduct thorough assessments of current practices to identify areas for improvement.
- Engagement and Training: Involve employees and provide training to foster a culture of sustainability.
- Monitor Progress: Establish KPIs and reporting mechanisms to track the effectiveness of sustainability initiatives.
Future Trends in Corporate Sustainability
Looking ahead, several trends are likely to shape the future of corporate sustainability:
- Increased Regulatory Pressures: Governments worldwide are imposing stricter environmental regulations, pushing companies to adopt more sustainable practices.
- Consumer Demand for Transparency: As consumers become more aware of sustainability issues, they are demanding greater transparency regarding corporate practices.
For additional insights into corporate sustainability, consider exploring resources from Sustainability Accounting Standards Board or Global Reporting Initiative.
By embracing these trends and best practices, organizations can not only navigate the complexities of corporate sustainability but also contribute positively to the planet and society as a whole.
