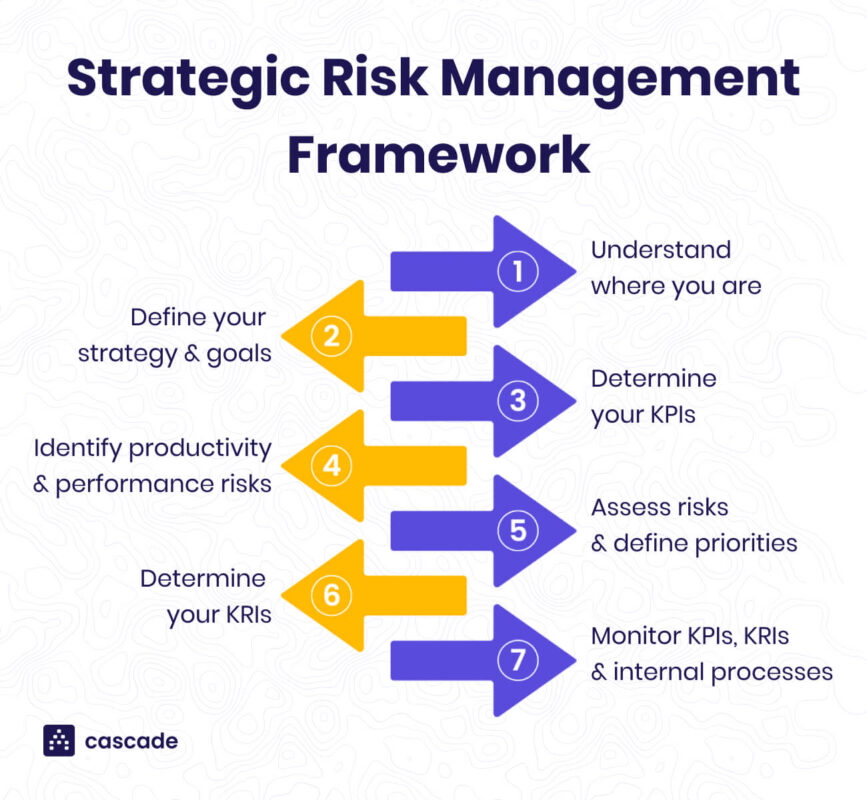
Understanding Risk Management Strategy
Risk management is an essential component of any successful business operation. In todays fast-paced and unpredictable environment, having a robust risk management strategy can be the difference between success and failure. This article will explore the key components of risk management, steps to develop a strategy, and tools that can help businesses effectively manage risks.

What is Risk Management?
Definition of Risk Management
Risk management involves identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks followed by coordinated efforts to minimize, monitor, and control the probability or impact of unfortunate events. Its not just about avoiding risks but also about making informed decisions that lead to strategic advantages.
Importance of Risk Management in Business
The significance of risk management cannot be overstated. Here are some compelling reasons why businesses should prioritize risk management:
- Protecting Assets: A well-defined strategy safeguards both physical and intangible assets from potential threats.
- Ensuring Compliance: Risk management ensures adherence to laws and regulations, helping avoid legal penalties and reputational damage.
- Enhancing Decision-Making: By understanding potential risks, leaders can make better-informed decisions that align with the companys objectives.
- Improving Business Resilience: Effective risk management prepares organizations for unexpected disruptions, ensuring continuity.
For more information on the principles of risk management, visit Investopedia.
Key Components of a Risk Management Strategy
Risk Identification
Identifying risks is the first step in creating an effective risk management strategy. This process involves recognizing potential hazards that could affect business operations.
Types of Risks
Understanding the different types of risks is crucial. They can broadly be categorized into:
- Financial Risks: These include market volatility, credit risks, and liquidity risks.
- Operational Risks: Related to internal processes, systems, or people.
- Strategic Risks: Risks that affect the businesss overall direction and objectives.
- Compliance Risks: Risks associated with legal and regulatory obligations.
Risk Assessment
Once risks are identified, the next step is to assess them. This involves evaluating the likelihood of occurrence and the potential impact on the business.
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Assessment
- Qualitative Assessment: This method involves subjective judgment and can include surveys or expert opinions.
- Quantitative Assessment: This involves statistical analysis and models to predict the likelihood and impact of risks.
Risk Mitigation
After assessing risks, businesses must develop strategies to mitigate them. This involves creating action plans to minimize the likelihood or impact of identified risks.
Strategies for Risk Mitigation
- Avoidance: Changing plans to sidestep potential risks.
- Reduction: Implementing measures to reduce the severity or likelihood of risks.
- Transfer: Shifting the risk to another party, such as through insurance.
- Acceptance: Recognizing the risk and preparing to deal with its consequences.

Risk Monitoring and Review
An ongoing process, risk monitoring involves regularly reviewing risk management strategies to ensure their effectiveness. This allows businesses to adjust their approaches in response to new risks or changes in the business environment.
Steps to Develop a Risk Management Strategy
Developing an effective risk management strategy involves several critical steps:
Step 1: Establish the Context
Understanding the internal and external environment in which the organization operates is vital for effective risk management. This includes identifying stakeholders and understanding their expectations.
Step 2: Identify Risks
Conduct thorough analyses and engage various departments to uncover all potential risks, ensuring no stone is left unturned.
Step 3: Analyze Risks
Evaluate how each risk can affect the organization. This can be done through both qualitative and quantitative assessments.
Step 4: Evaluate and Prioritize Risks
Not all risks are created equal. Prioritize them based on their potential impact and likelihood of occurrence, focusing resources on the most significant threats.
Step 5: Implement Risk Mitigation Strategies
Create an actionable plan that outlines how identified risks will be managed and mitigated.
Step 6: Monitor and Review
Continuously assess the effectiveness of risk management strategies, making adjustments as necessary to respond to evolving risks.
Tools and Techniques for Risk Management
There are various tools and techniques available to assist businesses in managing risks effectively:
Risk Management Software
Many organizations use specialized software to track, assess, and mitigate risks. These tools can streamline the risk management process, providing valuable data and insights.
Risk Assessment Matrix
A risk assessment matrix is a visual tool that helps prioritize risks based on their likelihood and impact, allowing organizations to focus on what matters most.
SWOT Analysis
Conducting a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) can provide a comprehensive overview of the internal and external factors affecting risk.
For more detailed methodologies, you may refer to this article on Risk Management Techniques.
This first half of the article sets a solid foundation for understanding risk management strategies while offering actionable insights and practical resources. The second half will explore common challenges, case studies, and answer frequently asked questions regarding risk management.
Common Challenges in Risk Management
Despite the importance of a risk management strategy, many organizations face challenges when implementing these processes. Recognizing these hurdles is the first step toward overcoming them.
Lack of Awareness and Understanding
One of the most significant obstacles is the lack of awareness and understanding of risk management principles within the organization. Many employees may not recognize the importance of identifying and managing risks, leading to a reactive rather than proactive approach.
Insufficient Resources
Risk management can require considerable resources, including time, personnel, and financial investment. Many organizations, especially smaller ones, may struggle to allocate sufficient resources to develop and implement effective risk management strategies.
Rapidly Changing Environment
In todays fast-paced business environment, risks can evolve rapidly. Companies must continuously adapt their risk management strategies to keep up with new technologies, regulatory changes, and market dynamics.
Resistance to Change
Organizational culture can play a significant role in the success of risk management initiatives. Resistance to change can hinder the implementation of new strategies and processes, preventing organizations from fully realizing the benefits of effective risk management.
Case Studies: Successful Risk Management Strategies
1. Coca-Cola: Embracing Technology for Risk Management
Coca-Cola has implemented advanced analytics and technology to enhance its risk management efforts. By leveraging data-driven insights, the company can identify potential risks across its supply chain and respond more effectively. This proactive approach has helped Coca-Cola maintain its market leadership even in challenging economic conditions.
2. Microsoft: Fostering a Risk-Aware Culture
Microsoft has cultivated a risk-aware culture by integrating risk management into its organizational framework. Employees are encouraged to identify and report risks, fostering an environment where risk management is seen as everyone’s responsibility. This culture not only enhances decision-making but also empowers employees to take ownership of their work.
3. JPMorgan Chase: Comprehensive Risk Framework
JPMorgan Chase has developed a comprehensive risk management framework that encompasses credit, market, and operational risks. The company utilizes sophisticated modeling techniques to assess risks and implement strategies to mitigate them effectively. This multifaceted approach has helped JPMorgan navigate economic downturns while safeguarding its assets.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the primary goal of a risk management strategy?
The primary goal of a risk management strategy is to identify, assess, and mitigate risks that could potentially harm the organization. By proactively managing risks, businesses can protect their assets, ensure compliance, and enhance decision-making.
How often should risk management strategies be reviewed?
Risk management strategies should be reviewed regularly, ideally on an annual basis or whenever there are significant changes in the business environment, such as new regulations, technological advancements, or shifts in market dynamics.
What are some common tools used in risk management?
Common tools used in risk management include:
– Risk assessment matrices
– Risk management software
– SWOT analysis
– Scenario analysis
– Heat maps
How can I foster a risk-aware culture in my organization?
To foster a risk-aware culture:
– Encourage open communication about risks.
– Provide training on risk management principles.
– Involve employees in the risk identification process.
– Recognize and reward proactive risk management efforts.
Conclusion
In an ever-evolving business landscape, developing a comprehensive risk management strategy is vital for long-term success. By understanding the key components of risk management, recognizing common challenges, and learning from successful case studies, organizations can position themselves to thrive despite uncertainties.
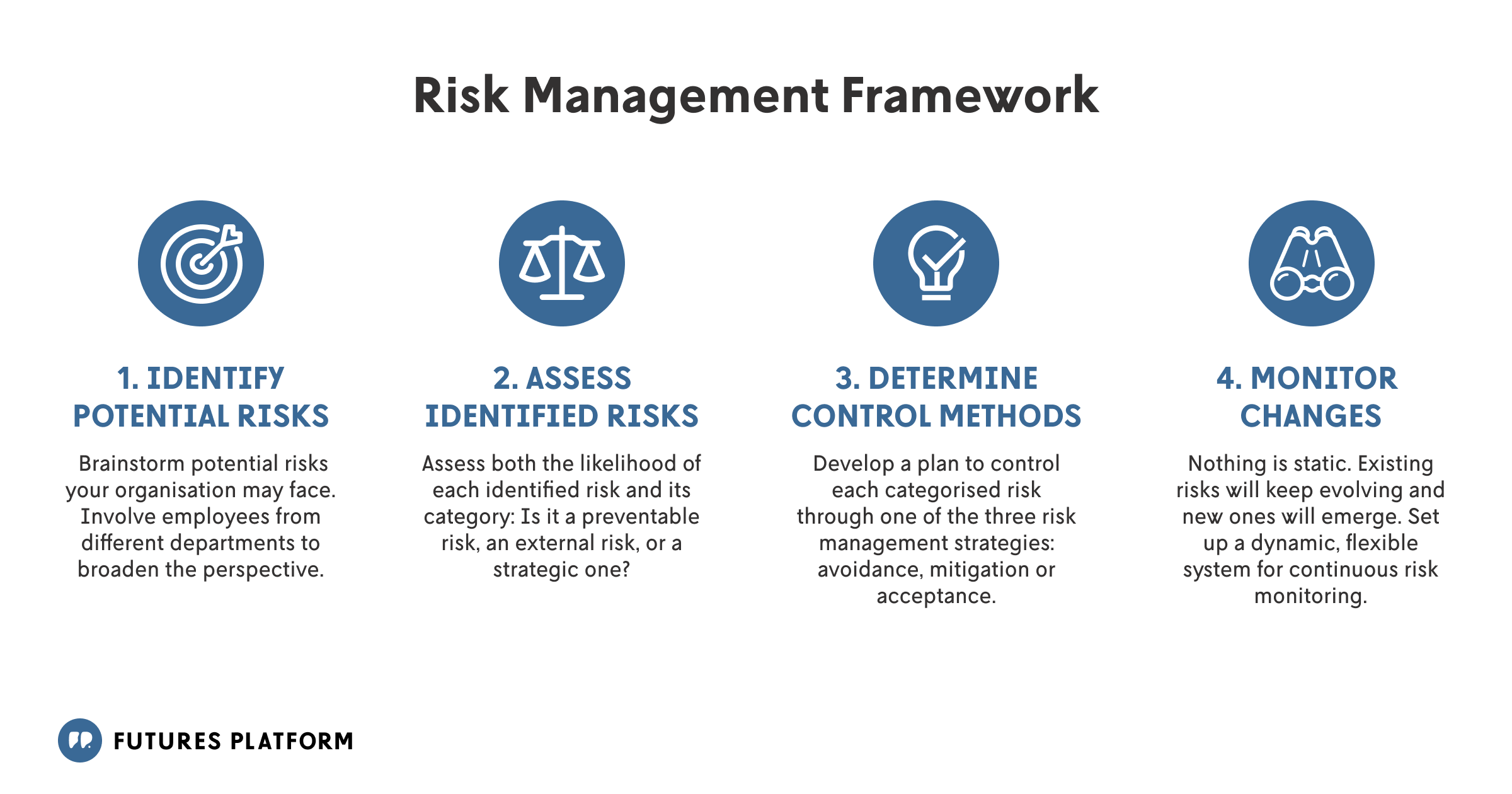
Additional Resources
For further reading on risk management techniques, consider exploring Hyperproof’s Risk Management Techniques. This resource provides an in-depth look at various methodologies that can enhance your organization’s risk management practices.
By adopting a proactive stance on risk management, your organization can not only protect itself from potential threats but also uncover new opportunities for growth and innovation. Embrace risk management as a strategic imperative and watch your organization flourish in the face of uncertainty.